Functions
Built-in functions
- PHP contains lots of built-in functions
- We restrict ourselves to some useful array, string and date functions
Array functions
- Complete list of array functions
- In the previous section, we already discussed the PHP array functions
array(),count()andcompact() - Open course/array_functions.php
<div class="margin-3">
<?php
$students = ['Doe, John' => 'r0662335', 'Doe, Jane' => 'r0715283', 'Smith, Jeff' => 'r0622915'];
$search = 'r0622915';
echo in_array($search, $students) ? "<p> Student with r-number $search was found!</p>\n" :
"<p> Student with r-number $search was not found!</p>\n";
?>
</div>
<div class="margin-3">
<?php
asort($students);
echo "<p> Students sorted by r-number: </p>\n";
echo "<ul>\n";
foreach ($students as $name => $student) {
echo "<li> $student: $name </li>\n";
}
echo "</ul>\n";
?>
</div>
<div class="margin-3">
<?php
ksort($students);
echo "<p> Students sorted by name: </p>\n";
echo "<ul>\n";
foreach ($students as $name => $student) {
echo "<li> $student: $name </li>\n";
}
echo "</ul>\n";
?>
</div>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
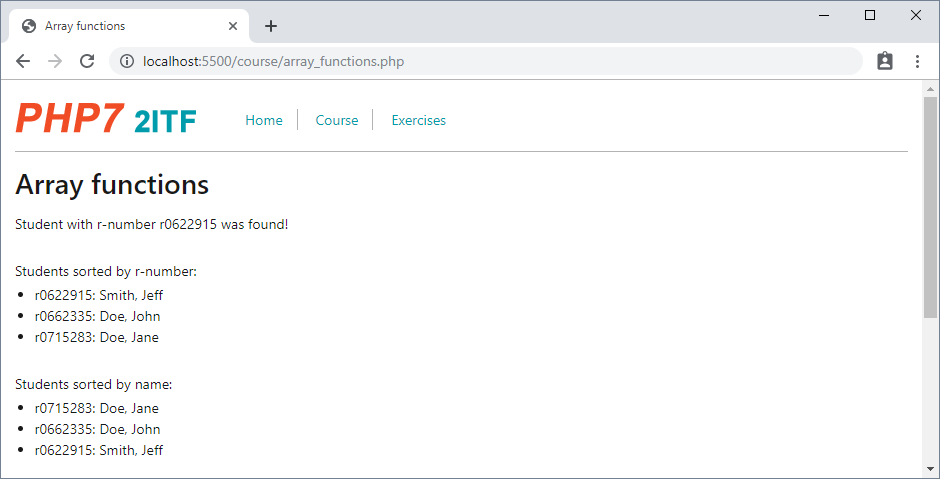
- The function
in_array($value, $array)checks if a specified$valueexists in an$array - The function
asort($array)sorts an$arrayand maintains the index association (important with associative arrays!) - The function
ksort($array)sorts an (associative)$arrayby key and maintains the index association
String functions
- Complete list of string functions
- Open course/string_functions.php
<div class="margin-3">
<?php
$testString = 'this is a random string to illustrate PHP string functions';
echo "<p> \$testString = '$testString' </p>\n";
echo "<p> Length of \$testString = " . strlen($testString) . "</p>\n";
echo "<p> Position (first occurrence!) of 'is' in \$testString = " . strpos($testString, 'is') . "</p>\n";
echo "<blockquote>Execute the statement <code>\$testString = ucfirst(\$testString);</code></blockquote>\n";
$testString = ucfirst($testString);
echo "<p> \$testString = '$testString' </p>\n";
echo "<blockquote>Execute the statement <code>\$subString = substr(\$testString, strpos(\$testString, 'P'), 3);</code></blockquote>\n";
$subString = substr($testString, strpos($testString, 'P'), 3);
echo "<p> \$subString = '$subString' </p>\n";
echo "<blockquote>Execute the statement <code>\$testString = str_replace('PHP', 'some', \$testString); </code></blockquote>\n";
$testString = str_replace('PHP', 'some', $testString);
echo "<p> \$testString = '$testString' </p>\n";
echo "<blockquote>Execute the statement <code>\$words = explode(' ', \$testString); </code></blockquote>\n";
$words = explode(' ', $testString);
echo "<p> \$words = </p>\n";
print_r($words);
?>
</div>
<hr>
<div class="margin-3">
<?php
$percentages = [64, 67.4598, 72.25, 76.9];
?>
<p>Numbers with 2 decimal digits and , as decimal point:</p>
<ul>
<?php
foreach ($percentages as $percentage)
echo "<li>" . number_format($percentage, 2, ',', '.') . "</li>\n";
?>
</ul>
</div>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
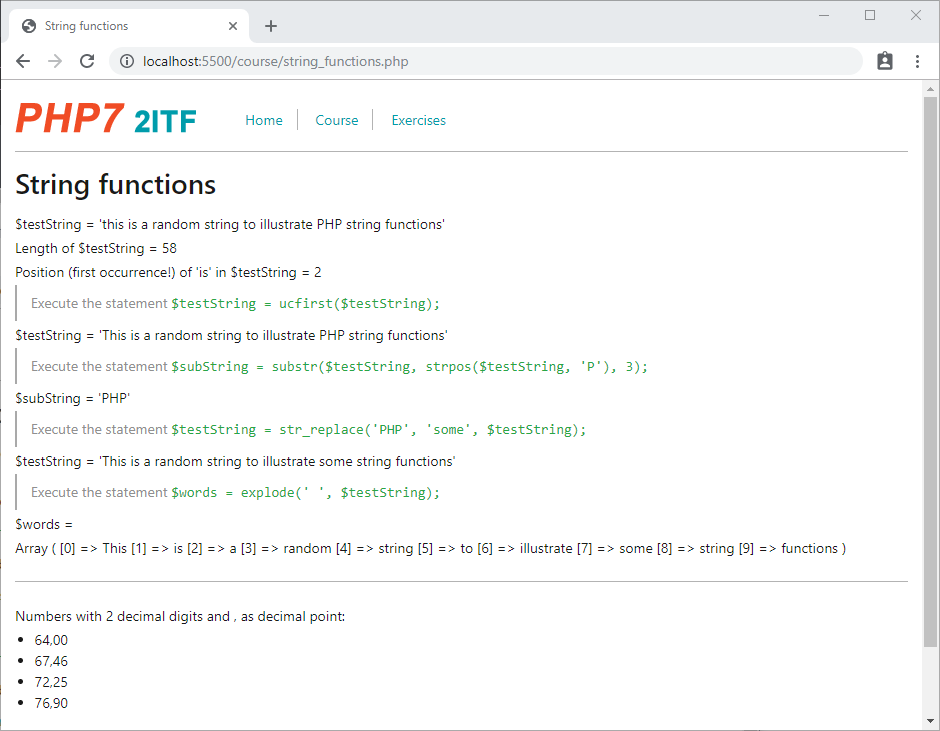
- The function
strlen($string)returns the length of$string - The function
strpos($haystack, $needle)returns the position of the string$needlein the string$haystack- Notice that the position of the first character in a string equals 0!
- The function
ucfirst($string)returns a string in which the first letter of$stringis capitalized - The function
substr($string, $start, $length)returns a portion (with$lengthcharacters) of$string, starting from position$start - The function
str_replace($search, $replace, $string)returns a string with all occurrences of$searchin$stringreplaced by$replace - The function
explode($delimiter, $string)returns an array of strings, each of which is a substring of$stringand which are separated by$delimiter - The function
number_format($number, $decimals, $decimalPoint, $thousandsSeparator)returns a string with a formatted version of$number, specified by the number of$decimals, the$decimalPointand the$thousandsSeparator- If the 2 last arguments (
$decimalPointand$thousandsSeparator) are omitted, the standard decimal point (.) and separator for thousands (,) are used
- If the 2 last arguments (
Date/time functions
- Complete list of date/time functions
- Open course/date_functions.php
<div class="margin-3">
<?php
$timestamp = mktime(0,0,0,12,25,2019); //25-12-2019, 0u00
echo "<p> Christmas 2019 (" . date("d/m/Y", $timestamp) . ") falls on a " . date("l",$timestamp). "</p>\n";
?>
</div>
<div class="margin-3">
<?php
echo "<p> Now, we are " . date("D d-m-Y, H:i:s") . "</p>\n";
echo "<p>" . mktime(date("H"),date("i"),date("s"), date("m"), date("d"), date("Y")) . " seconds have passed since January 1, 1970, 00:00:00 </p>\n";
$within4weeks = mktime(0,0,0, date("m"), date("d") + 28, date("Y"));
echo "<p> Within 4 weeks, we are " . date("l d F 'y", $within4weeks) . "</p>\n";
?>
</div>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
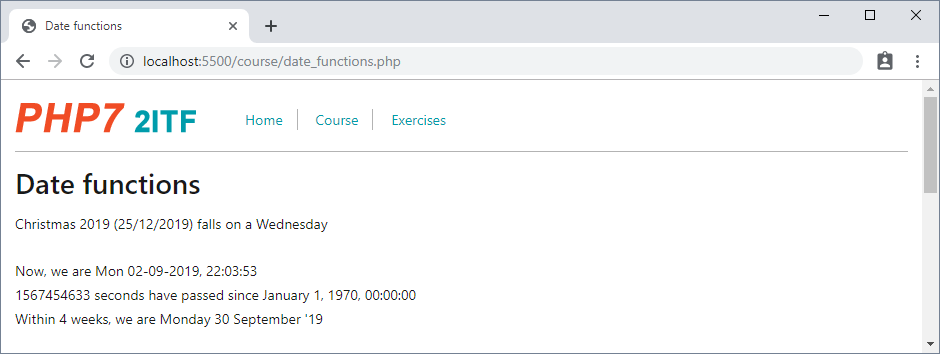
- Internally, PHP works with (Unix) timestamps to indicate dates and time
- A (Unix) timestamp is the number of seconds since January 1st, 1970 (00:00:00 GMT)
- A (Unix) timestamp can be created using the
mktime($hours, $minutes, $seconds, $month, $day, $year)function
- With the
date("format", $timestamp)function, this$timestampis converted into a readable format- Using date("format") - without timestamp - we get the current date/time on the server
- Some format characters:
| format character | description | values |
|---|---|---|
| d | day of the month with leading zeros | 01 - 31 |
| D | textual representation (three letters) of the day | Mon - Sun |
| j | day of the month without leading zeros | 1 - 31 |
| l | full textual representation of the day | Monday - Sunday |
| F | full textual representation of the month | January - December |
| m | numerical representation of the month with leading zeros | 01 - 12 |
| M | textual representation (three letters) of the month | Jan - Dec |
| n | numerical representation of the month without leading zeros | 1 - 12 |
| Y | numerical representation (4 digits) of a year | 1970, 2019 |
| y | numerical representation (2 digits) of a year | 70, 19 |
| h | 12-hour format with leading zeros | 01 - 12 |
| H | 24-hour format with leading zeros | 00 - 23 |
| i | minutes with leading zeros | 00 - 59 |
| s | seconds with leading zeros | 00 - 59 |
REMARK
Probably, there is a time difference between the depicted time (on the server) and the local time, because the timezone on the server is incorrect.
You can set the default timezone on the server to the correct timezone by adding the statement date_default_timezone_set('Europe/Brussels'), e.g. to the file shared/meta.php (included on every page).
User-defined functions
- Open course/user_defined_functions.php
<?php
function writeMessage(){
echo "<p> We hope you like this PHP course! </p>\n";
}
function writePersonalMessage($name){
echo "<p> Dear $name, we hope you like this PHP course! </p>\n";
}
function writePersonalMessageWithDefault($name = 'Mr./Mrs.'){
echo "<p> Dear $name, we hope you like this PHP course! </p>\n";
}
function subtractReduction20($price){
$price *= 0.8;
}
function subtractReduction30(&$price){
$price *= 0.7;
}
function average($number1, $number2){
return ($number1 + $number2)/2;
}
?>
<div class="margin-3">
<?php
writeMessage();
writePersonalMessage('John');
writePersonalMessageWithDefault('Jane');
writePersonalMessageWithDefault();
$price = 1000;
subtractReduction20($price);
echo "<p> Price with 20% reduction = " . $price . "</p>\n";
$price = 1000;
subtractReduction30($price);
echo "<p> Price with 30% reduction = " . $price . "</p>\n";
echo "<p> Average of 10 and 100 = " . average(10, 100) . "</p>\n";
?>
</div>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
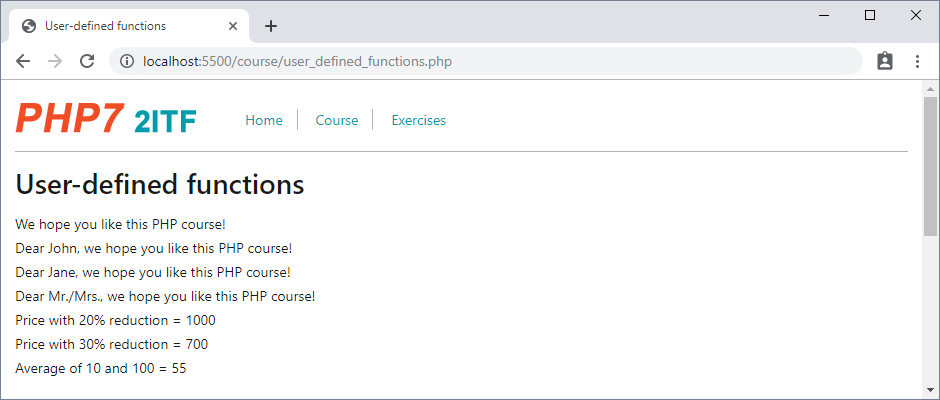
Functions without parameters
- A user-defined function (e.g.
function writeMessage()) starts with the keywordfunction, followed by( ) - The function code should be placed between
{ }
Functions with parameters
- Put the parameters of a function between the round brackets, as in
function writePersonalMessage($name) - When a function with parameters is called (e.g.
writePersonalMessage('John');), we need to supply arguments ('John') to pass to the parameters ($name) - These parameters work like variables inside your function
Default values for parameters
- You can set a parameter to have a default value if no argument is passed to the function, as in
function writePersonalMessageWithDefault($name = 'Mr./Mrs.")
By value versus by reference
- By default, arguments are passed by value
- This means that the original value of a variable is not changed when you pass it as an argument to a function in which it is changed. See e.g. function
function subtractReduction20($price)
- This means that the original value of a variable is not changed when you pass it as an argument to a function in which it is changed. See e.g. function
- You can pass a variable to a function by reference, meaning that the original value can be changed in the function
- In order to do so, precede the parameter in the function definition with
&, as illustrated infunction subtractReduction30(&$price)
- In order to do so, precede the parameter in the function definition with
Functions with return value
- A function can return a value using the return statement, as illustrated in
function average($number1, $number2)
Include
- Often, you want to use your self-written functions in different PHP files
- Move the function definitions to a separate file (e.g. course/my_functions.php)
- Include the content of this file (with the function definitions) in the file course/user_defined_functions.php with the statement
include_once 'my_functions.php'
REMARKS
- It's a good practice to use this technique (of including files) to include a navigation menu, a footer, ... on every page of your application
- In our project, shared meta-data (shared/meta.php), a navigation bar (shared/nav.php) and a footer (shared/footer.php) are included on every page
- Notice that we use relative paths in our
include_oncestatements (e.g.include_once('../shared/meta.php')).
You might want to tryinclude_once('/shared/meta.php'), but this doesn't work as in PHP the starting forward slash/does not correspond to the root of your project, but to the root of your filesystem on the server.
Useinclude_once($_SERVER['DOCUMENT_ROOT'] . '/shared/meta.php')to build up paths from the root of your project.
Read more on https://phpdelusions.net/articles/paths.